There was a time when managing our team’s customer requests felt like trying to catch a cascade of water with a sieve. Just as you address one, a handful more would appear, demanding attention. But then, Jira Service Management made its entrance. Imagine having the clarity where every single request, big or small, seamlessly fits into the process, waiting to be tracked and addressed. Those overwhelming days? A thing of the past. Want to know more about this shift? Let’s journey through JSM together.

What is Jira Service Management?
Jira Service Management, or JSM, isn’t just another face in the IT crowd. Picture JSM as the trusty compass in a landscape filled with tasks and requests. Instead of merely reacting, it empowers teams to anticipate needs, streamline operations, and act with precision. It’s all about turning the usual chaos into an elegant dance of productivity. If you’ve been looking for that secret ingredient to harmonize your team’s workflow, JSM might just be it.
Jira Service Management Feature
Peeling back the layers of Jira Service Management (JSM), it becomes evident that its strength lies in its robust suite of features, tailored to meet the diverse needs of modern teams:

1. Request Management
Handling customer requests is no small feat. With JSM’s Request Management, every query and demand is meticulously cataloged and addressed, ensuring consistency and efficiency.
2. Incident Management
Unforeseen incidents in the IT domain can disrupt workflows. JSM’s Incident Management ensures that such issues are swiftly identified, tackled, and resolved, upholding service continuity.
3. Change Management:
Implementing changes in an IT environment requires precision. JSM’s Change Management guides the assessment, approval, and smooth introduction of alterations to your processes or systems.
4. Asset Management:
Keeping track of both tangible and intangible assets is paramount. JSM’s Asset Management offers a comprehensive tracking system, ensuring optimal utilization and maintenance.
Read more about Asset Management in JSM: Atlassian Asset Management vs. AssetIT: Who Reigns Supreme in Inventory Tracking?
5. Configuration Management:
Harmonizing IT components to work in concert is essential. Configuration Management in JSM offers a methodical approach to organizing and integrating diverse IT elements.
6. Knowledge Management:
The power of information cannot be understated. JSM’s Knowledge Management centralizes team insights, making them organized and readily available, fostering continual learning.
7. Problem Management:
Addressing IT challenges requires a systematic approach. JSM’s Problem Management delves deep into identifying, analyzing, and effectively resolve underlying issues.
Each feature of JSM is meticulously designed, ensuring teams are equipped with the best tools to streamline their operations and achieve excellence.
Solution of Jira Service Management
JSM ensures that teams can deliver services efficiently. By optimizing workflows and reducing manual tasks, it empowers teams to address customer queries faster and more effectively.
With JSM, the barrier between IT operations and service delivery is bridged. By unifying these domains, teams can collaborate better and offer services that are in tune with IT capabilities.
By offering a user-friendly portal and ensuring quick response times, JSM enhances the overall customer experience, leading to higher satisfaction rates.
Before an issue escalates, JSM’s advanced analytics and monitoring capabilities can identify potential problems, allowing teams to resolve them preemptively.
Is Jira Service Management Right for Your Team?
Making the right choice in a sea of service management tools can be daunting. While Jira Service Management boasts a range of features, it’s essential to discern if it’s the perfect match for your team’s needs and goals. Here’s a guide to help you make that decision:
1. Evaluate Your Team’s Needs:
Complexity of Processes: If your team handles a multitude of tasks, from customer requests to internal IT incidents, JSM can offer the structure you need.
Integration Requirements: Do you frequently use other Atlassian products or third-party tools? JSM offers seamless integrations, enhancing the ecosystem of your tools.
2. Budget Constraints:
JSM, while robust, comes with a cost. Analyze the return on investment it offers against your budget. Remember to account for not just subscription costs but also potential training and onboarding expenses.
3. Team Adaptability:
Shifting to a new tool requires adaptability. Consider if your team is ready for the change and if they’ll be open to learning and navigating a new system.
4. Projected Growth:
Consider your organization’s future. If you foresee substantial growth, JSM’s scalability ensures it grows with you, accommodating increased demands.
5. Review & Feedback:
Reach out to peers in your industry who’ve adopted JSM. Their firsthand experiences and reviews can offer invaluable insights.
6. Test with a Trial:
Before making a long-term commitment, use JSM’s trial period. Engage your team during this phase, gather feedback, and assess if it genuinely streamlines your processes.
Analyze the resources Atlassian provides in terms of training and support. A strong support system can significantly ease the transition and adaptation process.
What is different between Jira Service Management and Jira Software or Jira Work Management
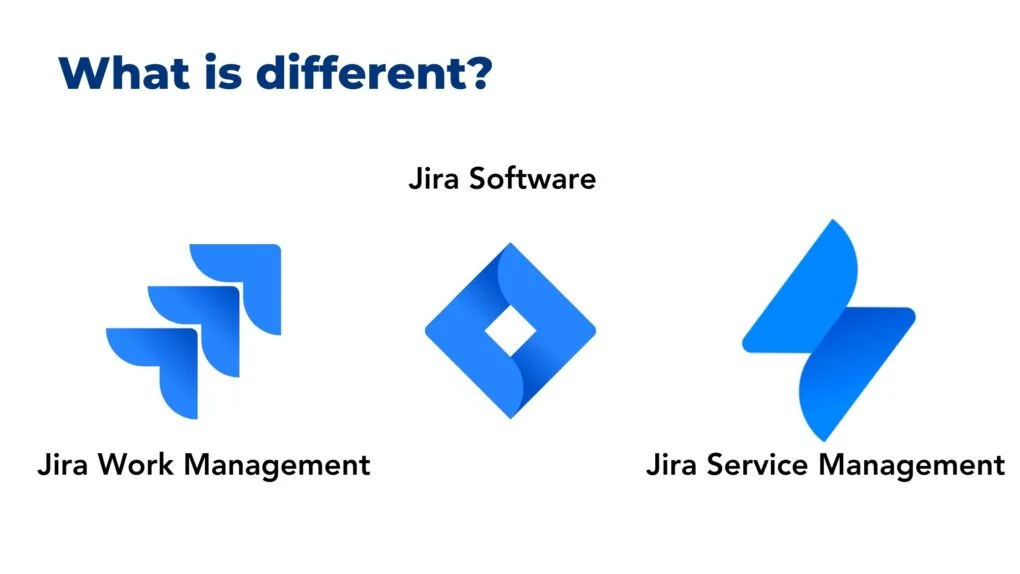
Jira Service Management (formerly Jira Service Desk)
Designed primarily for IT and service desk teams to manage and resolve service requests, incidents, and other ITSM (IT Service Management) processes.
Key Features:
- Service Request Management: Allows internal or external users to raise service requests through a portal.
- SLA Management: Ability to set and monitor Service Level Agreements.
- Incident, Problem, and Change Management: Aligns with ITIL practices to manage various IT processes.
- Asset Management: Integration with asset databases to track and manage assets.
- Knowledge Base Integration: Seamlessly integrates with Confluence to create a self-service portal for users.
Learn how to avoid asset management pitfalls with Assets in JSM at Avoid These 5 Crucial IT Inventory Tracking Pitfalls.
Jira Software:
Specifically designed for software development teams to plan, track, and release software.
Key Features:
- Agile Workflow: Supports Scrum, Kanban, and mixed methodologies with boards and sprint planning tools.
- Version and Release Management: Allows teams to plan releases and track progress.
- Developer Tool Integrations: Connects seamlessly with tools like Bitbucket, GitHub, and CI/CD pipelines.
- Custom Workflows: Enables teams to design workflows that mirror their software development processes.
- Code-Task Integration: Link commits, pull requests, and branches to tasks and stories.
Jira Work Management (formerly Jira Core):
Geared towards business teams (like HR, finance, marketing) to manage tasks, projects, and daily business processes.
Key Features:
- Custom Workflows: While simpler than Jira Software, Jira Work Management offers workflows tailored to business processes.
- Task and Project Tracking: Provides boards and lists to manage and monitor tasks.
- Templates: Offers project templates for various business use cases (e.g., project management, task tracking).
- Calendar Views: Allows users to view tasks and deadlines in a calendar format.
- Form Submissions: Facilitates capturing information through forms for business processes.
In essence:
- Jira Service Management is for teams providing services and support.
- Jira Software is for teams developing and releasing software.
- Jira Work Management is for business teams managing tasks, projects, and processes.
Learn more about Jira Software and Jira Work Management
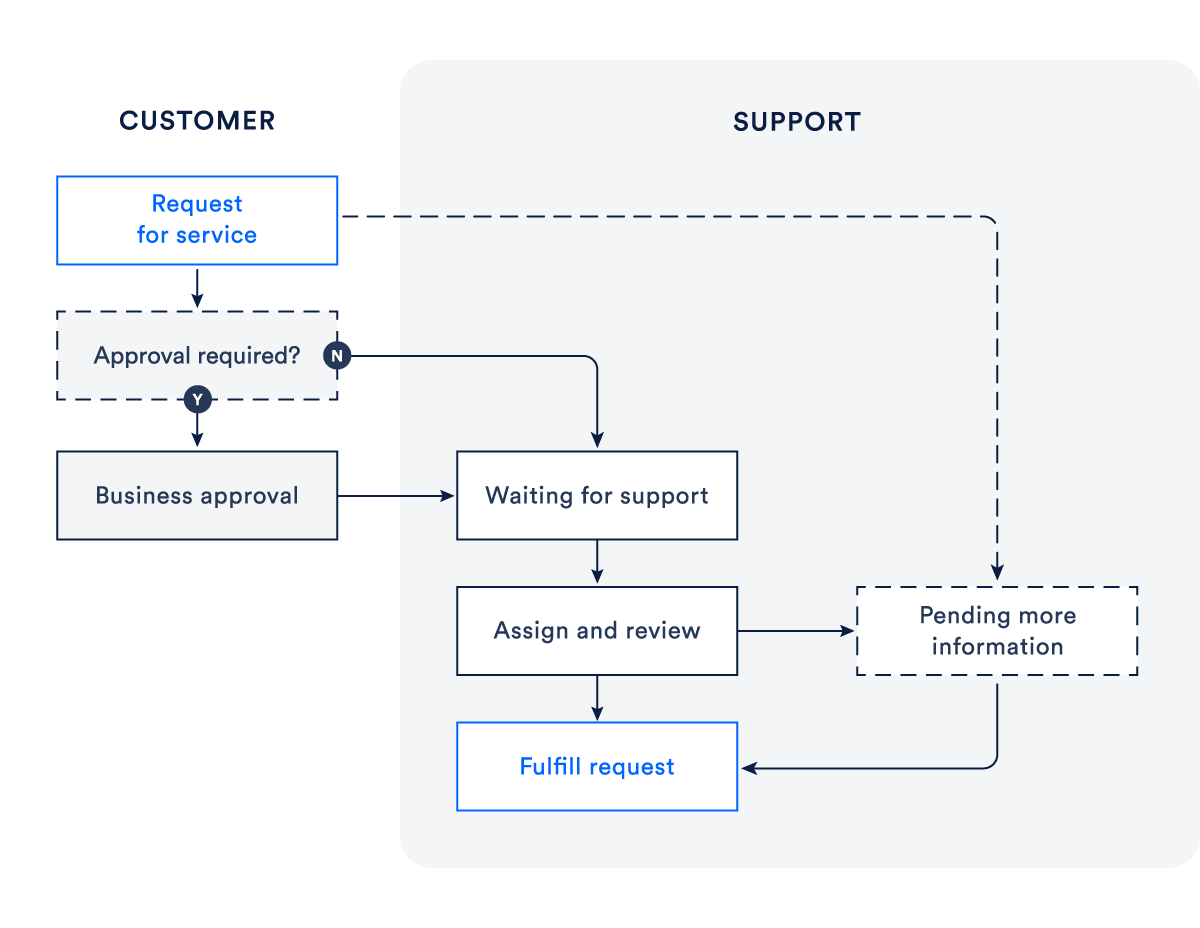
The service request management process in JSM
Here’s a breakdown of the service request management process in JSM:
1. Request Creation:
- User Portal: End-users or customers access the self-service portal to submit their service requests. The portal is user-friendly and customizable, often featuring categorized request types, such as “Report a Bug”, “Request New Hardware”, or “Access Issues”.
- Email: JSM can be configured to create requests directly from emails. When a user sends an email to a specified address, a new service request is automatically created.
- Embedded Widgets: Service request forms can be embedded in other platforms or websites to capture requests.
2. Triage & Prioritization:
- SLAs (Service Level Agreements): For each request type, JSM can apply predefined SLAs. These SLAs ensure that tickets are responded to and resolved within a specified time frame.
- Queues: Agents can view requests in customized queues, such as “High Priority” or “Pending Approval”. This helps agents quickly identify which requests need attention.
- Automation Rules: Automate the triage process, such as auto-assigning specific request types to particular agents or groups.
3. Request Processing:
- Collaboration: Agents can collaborate with team members, link related tickets, or mention other agents to get input on a particular request.
- Knowledge Base Integration: JSM integrates with Confluence to provide a knowledge base. If a solution exists in the knowledge base, agents can quickly reference or share it with the requester.
4. Communication:
- Notifications: JSM ensures stakeholders are informed at every step. Both agents and requesters receive notifications based on the ticket’s status and updates.
- Comments & Feedback: Agents can communicate with requesters directly through the ticket, seeking additional information or providing updates.
5. Resolution & Closure:
- Solutions: Once a solution is determined, agents can communicate this to the requester, ensuring they are satisfied with the outcome.
- Closure: After ensuring the requester’s issue is addressed, agents can close the ticket. Closed tickets are archived for future reference.
6. Reporting & Analysis:
- Dashboards: JSM provides dashboards that give insights into metrics like the volume of requests, resolution times, SLA breaches, and more.
- Feedback Collection: After ticket resolution, you can configure JSM to send satisfaction surveys to the users to collect feedback and continuously improve the process.
How to Get Started with Service Request Management in JSM
- Select Projects > Create project.
- Choose a service management template > Select Use template.
- Name your project.
- Create a project key or use the generated key.
- Choose if you would want to share settings with an existing project. If yes, specify the name of the existing project.
- Select Create project.
- Adjust the portal to your needs. You can create a self-service service desk by allowing your customers to edit requests by themselves and unbargain your agent. To make it happen, try out the extension Feature Bundle.
Navigating the world of service request management can sometimes feel like trying to find your way through a dense forest. But with Jira Service Management as your compass, the path becomes clearer. The insights we’ve unpacked in this blog are a testament to JSM’s versatility. But beyond the features and templates, it’s the difference it can make in real-world scenarios that truly resonates. Whether you’re just starting out or you’re a seasoned professional, there’s something in JSM for everyone. So, as you reflect on the needs of your team and the tales we’ve shared here, I encourage you to give JSM a try. Maybe, just maybe, it’ll be the tool that turns your service management challenges into tales of triumph.