Navigating the world of project management tools, Jira stands out with its two distinct offerings: Jira Cloud and Server versions. This blog delves into the essential differences between these options, guiding you through the nuances of Jira Cloud and how it contrasts with the traditional Server versions. Aimed at both new and seasoned Jira users, we’ll explore the features, benefits, and key decision-making factors of each version. Our goal is to provide a clear understanding of “Jira Cloud and Server Versions,” helping you choose the right tool for your project management needs.

Join us as we simplify this choice, ensuring you make an informed decision in your pursuit of enhanced team productivity and project management efficiency.
Table of Contents
Understanding Jira Cloud
What is Jira Cloud?
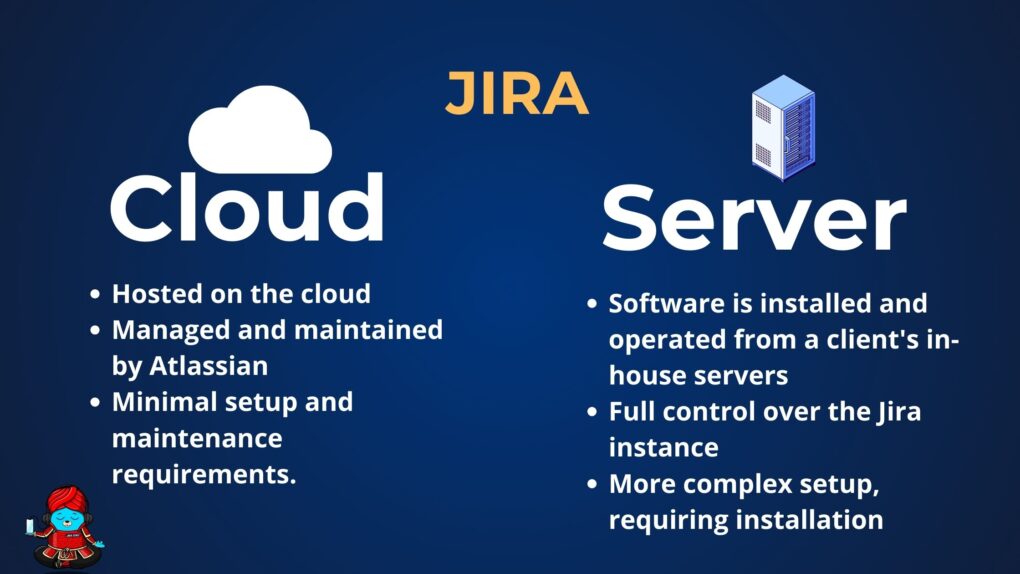
Jira Cloud represents the next generation of Jira software, hosted on the cloud. It’s a suite of cloud-based applications provided by Atlassian, designed to streamline project management, issue tracking, and agile processes. Unlike its on-premises counterpart, Jira Cloud is managed and maintained by Atlassian, offering users a hassle-free experience with minimal setup and maintenance requirements.
Key Features of Jira Cloud
- Automatic Updates and Maintenance: Jira Cloud automatically updates to the latest version, ensuring users have access to the newest features and security enhancements without any manual intervention.
- Accessibility: Being cloud-based, Jira Cloud can be accessed from anywhere, at any time, provided there’s an internet connection. This accessibility facilitates remote and distributed teams to collaborate effectively.
- Integrated Solutions: Jira Cloud comes with seamless integration capabilities with other Atlassian products like Confluence and Trello, and a vast array of third-party apps available in the Atlassian Marketplace.
- Scalability: It offers high scalability options, suitable for businesses of all sizes. As your team grows, Jira Cloud can easily accommodate the increasing workload and user count.
Benefits of Jira Cloud
- Ease of Use: With its intuitive interface and reduced need for technical maintenance, Jira Cloud is user-friendly, even for those with limited technical expertise.
- Security and Compliance: Atlassian ensures high-level security standards and compliance with various certifications, making Jira Cloud a secure choice for sensitive projects.
- Cost-Effectiveness: With a subscription-based model, Jira Cloud eliminates the upfront costs associated with server-based solutions and reduces the ongoing maintenance expenses.
- Innovation and Collaboration: Regular updates mean teams always have the latest tools at their disposal, fostering innovation and collaboration.
Target Audience and Use Cases
Jira Cloud is ideal for teams that prefer a plug-and-play solution with minimal infrastructure management. It’s particularly suited for small to medium-sized businesses or teams that work remotely. Common use cases include agile project management, software development, task tracking, and cross-team collaboration.
Exploring Jira Server
What is Jira Server?
Jira Server refers to the on-premises version of Jira, where the software is installed and operated from a client’s in-house servers. This version gives organizations full control over the Jira instance, including its maintenance, upgrades, and data storage. Jira Server is tailored for businesses that prefer or require direct control over their data and infrastructure due to regulatory, security, or specific operational needs.
Key Features of Jira Server
- Customization and Control: Users have complete control over their Jira environment, allowing for extensive customization and integration with internal systems.
- Data Management: With Jira Server, data is stored on-site, providing organizations with direct control over their data security and management protocols.
- Performance Optimization: Companies can optimize the performance of Jira Server to meet their specific needs, depending on their server capacity and configuration.
- One-Time Licensing Fee: Jira Server is available through a one-time licensing fee, which can be a cost-effective solution for organizations willing to manage their own servers.
Benefits of Jira Server
- Data Sovereignty: Ideal for organizations with stringent data control and privacy requirements, offering complete data sovereignty.
- Customizability: Provides a high degree of customization and flexibility in terms of both functionality and integration with other internal systems.
- Offline Access: Being an on-premises solution, Jira Server can be accessed without an internet connection, ensuring availability even in offline scenarios.
- No Recurring Costs: Apart from maintenance and running costs, there are no recurring subscription fees, making it a potentially cost-effective option in the long term.
Target Audience and Use Cases
Jira Server is particularly well-suited for large enterprises with specific compliance requirements, or those with existing infrastructure and resources to support on-premises solutions. Common use cases include project management in regulated industries, businesses with high data sensitivity, and organizations seeking deep integration with internal systems.
Comparative Analysis: Jira Cloud vs Jira Server
Understanding the key differences between Jira Cloud and Jira Server is crucial for organizations when deciding which platform best suits their needs. This section provides a comparative analysis across various critical aspects.
1. Installation and Setup
- Jira Cloud: Requires minimal setup, with no installation necessary. Users can start almost immediately after subscribing.
- Jira Server: Involves a more complex setup, requiring installation on the company’s servers and ongoing maintenance by an IT team.
2. Data Security and Privacy
- Jira Cloud: Managed by Atlassian, with robust security measures in place. However, data is stored off-premises, which might not suit organizations with stringent data control policies.
- Jira Server: Offers complete control over data security, as all data is stored on the organization’s own servers, aligning with specific compliance and privacy requirements.
3. Customizability and Integration
- Jira Cloud: Offers a range of customization options and integrations, but some limitations exist compared to the Server version.
- Jira Server: Provides extensive customization and integration capabilities, allowing organizations to tailor the software to their specific needs.
4. Cost and Pricing Models
- Jira Cloud: Operates on a subscription-based model, which can be more cost-effective for small to medium-sized businesses without the infrastructure to support an on-premises solution.
- Jira Server: Involves a one-time licensing fee, plus the costs of maintaining servers and infrastructure, which can be more economical for larger organizations in the long run.
5. Performance and Reliability
- Jira Cloud: Performance is dependent on internet connectivity. Atlassian ensures high uptime and reliability.
- Jira Server: Performance can be optimized based on the organization’s server capacity. Reliability is dependent on the company’s IT infrastructure.
6. Maintenance and Support
- Jira Cloud: Atlassian handles maintenance, with automatic updates and support.
- Jira Server: Requires internal maintenance and manual updates, often necessitating a dedicated IT team.
Compare Atlassian cloud vs server
Jira Server and Data Center feature comparison
Pros and Cons of Each Version
Understanding the advantages and disadvantages of both Jira Cloud and Jira Server is vital for organizations to make an informed decision. Here’s a breakdown of the pros and cons of each version:
Jira Cloud
Pros:
- Ease of Setup and Maintenance: With Jira Cloud, there’s no need for extensive setup or maintenance, as Atlassian manages these aspects.
- Automatic Updates: Users always have access to the latest features and security updates without any manual intervention.
- Accessibility: Being cloud-based, it is accessible from anywhere, enhancing collaboration, especially for remote teams.
- Scalability: Easily scalable to accommodate growing teams or increased workload.
- Integrated Solutions: Offers seamless integration with other cloud-based Atlassian products and third-party apps.
Cons:
- Less Control Over Data: Since the data is hosted in the cloud, organizations have less control over their data security and management.
- Customization Limitations: There are some constraints in customization compared to the Server version.
- Dependent on Internet Connectivity: Performance is reliant on internet access, which can be a limitation in areas with poor connectivity.
- Ongoing Subscription Costs: While initially cost-effective, the subscription costs can accumulate over time.
Jira Server
Pros:
- Complete Data Control: Offers total control over data storage and security, complying with strict data policies.
- High Customizability: Allows extensive customization and deeper integration with internal systems and workflows.
- One-Time Licensing Fee: Can be more cost-effective in the long run, especially for larger organizations with the necessary infrastructure.
- Offline Access: Accessible without an internet connection, ensuring continuous operation.
Cons:
- Resource-Intensive: Requires significant infrastructure and an IT team for installation, maintenance, and updates.
- Initial Investment: Higher upfront costs due to licensing and server setup.
- No Automatic Updates: Manual updating can be time-consuming and requires additional IT resources.
- Scalability Challenges: Scaling up may require additional hardware and resources.
Transition from Server to Cloud (if applicable)
As the tech world increasingly leans towards cloud-based solutions, many organizations using Jira Server are contemplating a transition to Jira Cloud. This shift can bring about significant changes in how teams manage their projects and data. Understanding the implications and process of this transition is crucial for a smooth changeover.
Steps for Transitioning from Server to Cloud
- Assessment and Planning: Conduct a thorough assessment of current server setup, data, and workflows. Plan the migration in phases, if necessary, to minimize disruption.
- Choosing the Right Plan: Select a Jira Cloud plan that aligns with the organization’s size and needs.
- Data Migration: Utilize tools provided by Atlassian or third-party services for efficient data migration.
- Testing and Validation: Ensure all data and workflows function as expected in the cloud environment.
- Training and Support: Provide comprehensive training and support to team members for a smooth adaptation to Jira Cloud.
Future of Jira: Cloud vs Server
As the landscape of project management tools evolves, understanding the future trajectory of Jira Cloud and Server versions is essential for organizations planning their long-term project management strategy.
Trends and Future Developments in Cloud Computing
- Increased Adoption of Cloud Services: The trend towards cloud computing continues to grow, with more businesses adopting cloud solutions for their scalability, flexibility, and cost-effectiveness.
- Advancements in Security and Compliance: As cloud platforms mature, enhancements in security and compliance features are making cloud solutions more attractive, even for highly regulated industries.
- Integration with Emerging Technologies: Cloud platforms are increasingly integrating with emerging technologies like AI and machine learning, offering advanced analytics and automation capabilities.
Predictions About the Future of Jira Server
- Focus on Cloud: Atlassian has been increasingly focusing on its cloud offerings, suggesting a gradual shift away from on-premises solutions.
- Limited Development for Server Versions: There may be slower development and fewer new features for the Server versions compared to the Cloud.
- Sustained Niche Demand: Despite the cloud’s growing dominance, there will likely remain a niche market for Server versions, particularly among organizations with specific regulatory or data sovereignty needs.
How These Trends Affect Users’ Choice
- Cloud as a Mainstream Solution: Organizations, especially those growing or with remote teams, might find Jira Cloud more aligned with future technological trends and workplace dynamics.
- Server Versions for Specialized Needs: Entities with specific compliance, security, or customization requirements may continue to find value in Jira Server.
- Cost and Resource Considerations: The choice between Cloud and Server may also be influenced by long-term cost considerations and available IT resources.
in short, Jira Cloud is a version of Jira that is hosted and managed by Atlassian on the cloud. This means users do not need to install or maintain the software on their own servers. Jira Cloud offers automatic updates, easier management, and access from anywhere through the internet.
Jira Server, on the other hand, is a version of Jira that users install and manage on their own servers. This allows for deeper customization and full control over data and system configuration. However, it requires IT resources for maintenance and software updates.
The main difference between Jira Cloud and Jira Server lies in the location of hosting and management: Jira Cloud is managed on the cloud by Atlassian, while Jira Server is directly managed by the users on their own servers.
FAQs
Can I switch from Jira Server to Cloud?
Yes, Atlassian provides a migration path for transitioning from Jira Server to Cloud. This process involves planning, data migration, and adaptation to the new platform.
Is Jira Cloud more secure than Jira Server?
Jira Cloud adheres to high security and compliance standards managed by Atlassian. However, Jira Server offers more control over security, as data is stored on-premises. The security preference depends on an organization’s specific requirements.
Will my existing integrations work with Jira Cloud?
Many integrations available for Jira Server also work with Jira Cloud, but it’s important to verify each integration, as there may be some differences in compatibility.
What is the cost difference between Jira Cloud and Server?
Jira Cloud operates on a subscription model, while Jira Server involves a one-time licensing fee plus the costs of server maintenance. The total cost depends on the organization’s size and infrastructure.
How does performance compare between Jira Cloud and Server?
Atlassian manages Jira Cloud’s performance, which depends on internet connectivity. Organizations can optimize Jira Server’s performance based on their IT infrastructure.
Is Jira Server being phased out?
While Atlassian is focusing more on cloud solutions, Jira Server currently remains a supported option, especially for organizations with specific needs that cloud solutions cannot meet.
Learn more:
Register & Get Started with Jira Software